
“The shift towards precision medicine is supported by significant advances in biomarker testing, with next generation sequencing allowing the detection of genomic alterations which drive tumour development and providing critical insights into a patient’s likely response to treatment and progression of disease.” – EFPIA1
Personalized medicine is transforming healthcare, offering solutions tailored to individual needs. As part of our Global Personalized Medicine Series, this post explores Europe, a region renowned for its collaborative spirit, cutting-edge research, and robust policy frameworks. From life sciences innovations to overcoming regulatory hurdles, Europe demonstrates a unique approach to precision healthcare.
This is Part 2 of a 4-part series, with previous coverage focused on the United States.
In this installment, we’ll examine Europe’s journey, highlight key case studies, and predict what lies ahead for the region.
The State of Personalized Medicine in Europe
Policy and Frameworks
The European Union (EU) recognizes the potential of personalized medicine, embedding it in policies like the EU Health Policy Platform. Programs such as Horizon Europe allocate substantial funding to support projects integrating genomics and artificial intelligence (AI) for patient care. For example, Horizon 2020, its predecessor, allocated nearly €80 billion from 2014-2020 to various research and innovation projects, many of which advanced personalized healthcare.
Horizon Europe

Horizon Europe is the European Union’s flagship research and innovation programme for 2021–2027, with an indicative budget of €93.5 billion. It aims to tackle climate change, achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, and boost the EU’s competitiveness and growth5. Building on the success of Horizon 2020, Horizon Europe introduces initiatives like the European Innovation Council to support breakthrough innovations.
As of 2023, significant progress includes the launch of numerous projects under its various pillars, fostering collaboration across member states7. The programme continues to adapt, reallocating resources to address emerging challenges such as the European Chips Act and support for Ukraine.
Collaboration and Data Sharing
Europe excels in collaboration. The 1+ Million Genomes Initiative8 brings together 23 countries to create a shared genomic database by 2025. This initiative aims to enable cross-border healthcare improvements while protecting patient privacy under GDPR, which establishes a balance between innovation and data protection.
Case Studies of European Leaders
Europe’s advancements in personalized medicine are driven by pioneering organizations and national initiatives. Here’s how key players and countries are contributing:
1. Horizon Europe’s EP PerMed Partnership

The European Partnership for Personalised Medicine (EP PerMed) unites over 30 countries and diverse stakeholders to harmonize personalized medicine research across Europe. With a total budget of around €375 million, provided by the EU and more than 50 international partners, EP PerMed will not only significantly support the transnational development of personalised medicine approaches over the next ten years, but also their successful translation into clinical practice10.
- Projects like the Beyond 1 Million Genomes initiative have supported data-sharing infrastructures to sequence and utilize genomic data effectively, targeting cancer and rare diseases.

- Such initiatives are bringing Europe closer to reaching the goal of enabling secure access to genomic data across borders to advance research and personalised care in Europe. By 2024, at least six EU countries were expected to have implemented common specifications and will be able to manage genomic data access. By 2026, 15 countries will have an operational infrastructure in place.13
2. UK’s Oxford Nanopore Technologies and Genomics England
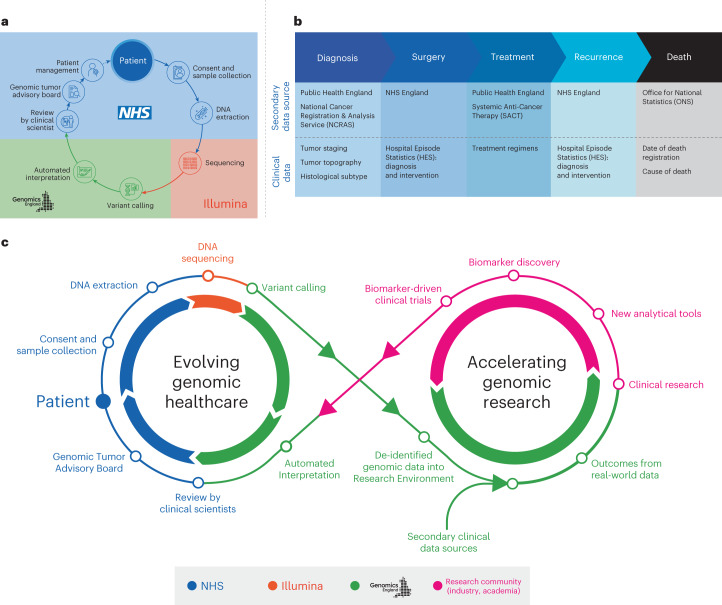
Oxford Nanopore has revolutionized genomic sequencing with portable devices like MinION, enabling real-time sequencing. Partnering with Genomics England, this technology is integral to the 100,000 Genomes Project, targeting rare diseases and cancers.

- Oxford Nanopore’s sequencing has facilitated rapid genomic insights in clinical settings, improving diagnostic efficiency. This has led to deep impacts in the fields of biodiversity conservation, elevated organ transplant success rate, expansion in disease characterization, revolution in critical care17.
- Genomics England, alongside NHS England, analyzed WGS data from 13,880 solid tumors spanning 33 cancer types, integrating genomic data with real-world treatment and outcome data, within a secure Research Environment. Study findings demonstrate the utility of linking genomic and real-world clinical data to enable survival analysis to identify cancer genes that affect prognosis and advance our understanding of how cancer genomics impacts patient outcomes.
3. France’s AI-Driven Efforts and Sophia Genetics

France’s “AI for Health” program integrates AI into personalized care, particularly for oncology. Sophia Genetics, a Swiss-French company, collaborates with hospitals to analyze genomic data for actionable insights.
- Sophia Genetics’ AI-driven algorithms enhance the precision of diagnostic tools for rare diseases and cancers.
- In 2024 Q3, 462 customers performed 91,000 analyses on SOPHiA DDMTM21 .
4. Germany’s Genomic Medicine Alliance and Roche Innovations
Germany’s Alliance for Genomic Discovery initiative integrates genomic sequencing into clinical care, supported by companies like Roche, which provides diagnostic tools and targeted therapies. Roche’s collaboration with German healthcare providers focuses on oncology and rare diseases.

Roche’s companion diagnostics have optimized cancer therapies, reducing adverse effects and improving survival rates.
5. Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet and AstraZeneca Partnership
This partnership highlights the integration of research and clinical efforts for oncology therapies. Utilizing molecular profiling technologies, they have refined cancer treatment pathways.

Sweden’s PROMISE initiative (Precision Omics Initiative Sweden) is a new transformative initiative that will be centered around SciLifeLab and Genomic Medicine Sweden (GMS) to completely integrate medical research with the healthcare system in Sweden29.
PROMISE will have three major focus areas:
- Generate extensive multi-omics data from both patients and the general population in Sweden,
- Develop a strong and effective infrastructure to integrate healthcare generated multi-omics data for research applications, improve data sharing and data accessibility across Sweden,
- Develop legal and regulatory frameworks for better alignment with modern capabilities, for maximum utilization of Sweden’s great potential.
Challenges Europe Faces in Scaling Precision Medicine
Implementing precision medicine in Europe presents several challenges that impede its widespread adoption. Key obstacles include:
1. Data Privacy and Sharing Regulations
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforces strict guidelines on personal data usage, complicating the sharing of health information essential for precision medicine30. These regulations can hinder international collaboration and data exchange necessary for research and treatment development.
2. Fragmented Healthcare Systems
Europe’s diverse healthcare infrastructures lead to inconsistencies in implementing precision medicine. Variations in diagnostic capabilities and treatment protocols across countries create disparities in patient access to personalized therapies.
3. Ethical and Legal Considerations
Precision medicine raises ethical issues, particularly concerning informed consent and the use of genetic information31. Ensuring patients understand and agree to the use of their data for research purposes is complex, especially with varying levels of health literacy.
4. Economic Constraints
The high cost of developing and implementing personalized treatments poses economic challenges. Health systems must balance the benefits of innovative therapies with budgetary limitations, which can affect the availability of precision medicine services.
5. Technological Integration
Integrating advanced technologies into existing healthcare systems requires significant investment and training. The need for standardized data formats and interoperable systems is critical to facilitate the effective use of precision medicine tools.32
Predictions for Europe’s Personalized Medicine Future
Europe is actively advancing personalized medicine through strategic programs and evolving regulations.
Short-Term Projections (1–3 Years):
The European Partnership for Personalised Medicine (EP PerMed34), launched under Horizon Europe, aims to coordinate and promote research in personalized medicine across EU member states and associated countries35. This partnership involves ministries responsible for research, innovation, and health policy, as well as national and regional healthcare authorities.
Additionally, the European Commission’s communication on enabling the digital transformation of health and care identifies personalized medicine through shared European data infrastructure as a key priority. This initiative focuses on citizens’ secure access to their health data across borders and the use of shared data infrastructures to advance personalized medicine.
Medium-Term Projections (3–7 Years):
The European Union’s Clinical Trials Regulation aims to simplify the conduct of clinical trials, facilitating research in therapies using personalized medicine. This regulatory framework is expected to streamline the approval process for new treatments, enhancing the development and availability of personalized therapies.
Furthermore, the European Commission has identified personalized medicine as a priority area, with initiatives aimed at promoting research and innovation in this field. The focus includes data sharing and eHealth, with the goal of enabling the digital transformation of health and care in the digital single market.
Long-Term Projections (7–15 Years):
By 2040, personalized medicine is expected to be fully integrated into Europe’s healthcare systems, supported by sustained investment and collaborative efforts. The European Commission has been investing in personalized medicine research since 2010, with a total of €3.2 billion invested across various projects38. This long-term commitment is anticipated to lead to significant advancements in personalized treatment approaches and the consolidation of personalized medicine within health systems.
These projections underscore Europe’s dedication to advancing personalized medicine through strategic initiatives and regulatory frameworks, aiming to improve healthcare outcomes for its citizens.
Conclusion
Europe’s personalized medicine revolution offers valuable lessons in collaboration, innovation, and balancing patient privacy with medical progress. As we continue this series, our next post will focus on the Asia-Pacific region, where dynamic growth and technological advancements create unique opportunities for personalized healthcare.
What are your thoughts on Europe’s role in shaping the future of precision medicine? Share your insights in the comments below, and stay tuned for the next part of this series.
References
- https://www.efpia.eu/media/589727/unlocking-the-potential-of-precision-medicine-in-europe.pdf ↩︎
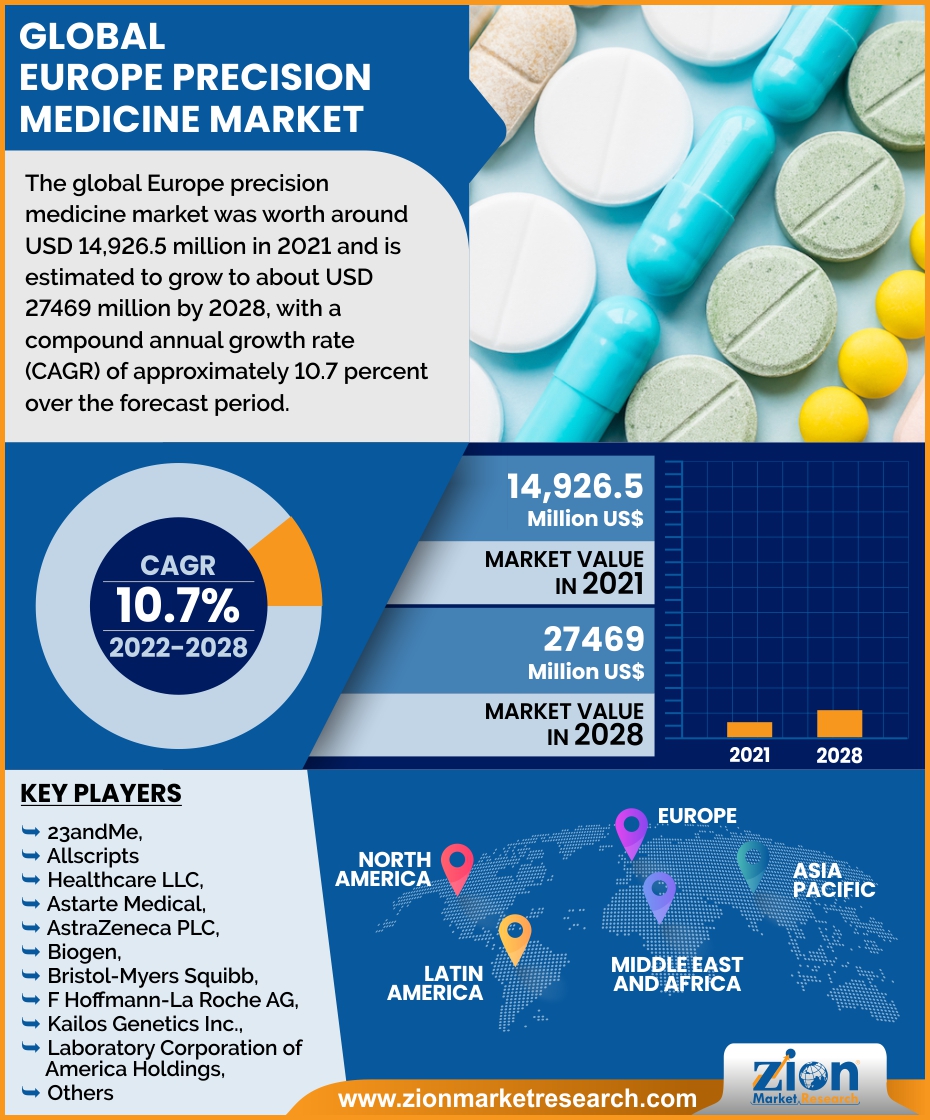
- https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/report/europe-precision-medicine-market ↩︎
- https://sciencebusiness.net/news/newer-member-states-facing-conundrum-extracting-value-horizon-europe ↩︎
- https://europoshorizontas.lt/en/horizon-europe-programme/ ↩︎
- https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/funding/funding-opportunities/funding-programmes-and-open-calls/horizon-europe_en ↩︎
- https://projects.research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/en/knowledge-publications-tools-and-data/interactive-reports/performance-european-partnerships-2022 ↩︎
- https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/eu-budget/performance-and-reporting/programme-performance-statements/horizon-europe-performance_en ↩︎
- https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/1-million-genomes ↩︎
- https://www.eppermed.eu/about-ep-permed/mission-objectives/ ↩︎
- https://www.eppermed.eu/news-events/news/new-european-partnership-for-personalised-medicine-ep-permed-established/ ↩︎
- https://www.eppermed.eu/publications-resources/additional-resources/other-pm-related-projects-initiatives/ ↩︎
- https://b1mg-project.eu/resources/ ↩︎
- https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/1-million-genomes ↩︎
- https://www.biotechniques.com/companies/oxfordnanoporetech-2/ ↩︎
- https://research.genomicsengland.co.uk/news/genomics-england-research-portal-launched/ ↩︎
- https://www.technologyreview.com/technology/nanopore-sequencing/ ↩︎
- https://nanoporetech.com/about/environmental-social-responsibilities/global-impact ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10803271/ ↩︎
- https://www.sophiagenetics.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.sophiagenetics.com/technology/ ↩︎
- https://www.sophiagenetics.com/news/sophia-genetics-reports-third-quarter-2024-results/ ↩︎
- https://www.roche.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.ghga.de/mission/partners ↩︎
- https://reform-support.ec.europa.eu/what-we-do/health-and-long-term-care/integrating-genomics-healthcare-genomde_en ↩︎
- https://www.bundesgesundheitsministerium.de/en/en/international/european-health-policy/genomde-en.html ↩︎
- https://tethys.pnnl.gov/organization/karolinska-institutet ↩︎
- https://www.astrazeneca.se/ ↩︎
- https://news.ki.se/successful-implementation-of-precision-medicine-at-a-national-level ↩︎
- https://www.scilifelab.se/event/precision-omics-initiative-sweden-promise-symposium/ ↩︎
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41431-023-01403-y ↩︎
- https://www.mdpi.com/1718-7729/31/12/592 ↩︎
- https://jnjinnovation.com/news/blog-post/precision-health-medicine–opportunities–challenges?utm_source=chatgpt.com ↩︎
- https://www.tritonmarketresearch.com/reports/europe-precision-medicine-market ↩︎
- https://www.eppermed.eu/ ↩︎
- https://www.horizon-europe.gouv.fr/european-partnership-personalised-medicine-33730 ↩︎
- https://www.eppermed.eu/news-events/news/first-in-situ-visit-for-ep-permed-at-swedish-personalised-medicine-centres/ ↩︎
- https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/europe-gene-therapy-market ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29749834/ ↩︎









Leave a comment