
Precision medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by shifting the focus from a one-size-fits-all approach to highly individualized treatment strategies
Unveiling the Path to Personalized Healthcare
The world of healthcare is witnessing a revolution, and at its helm is personalized medicine. As the first installment in a four-part series, this post explores how the U.S. healthcare ecosystem has emerged as a pioneer in this field, leveraging technological innovation and patient-centric care models.

In future posts, we will traverse Europe, Asia, and emerging markets to understand their contributions to this transformative journey.
Personalized Medicine

Defining Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, tailors healthcare to individual patients based on their unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle profiles. This approach moves beyond one-size-fits-all treatments, delivering improved outcomes and reduced side effects.
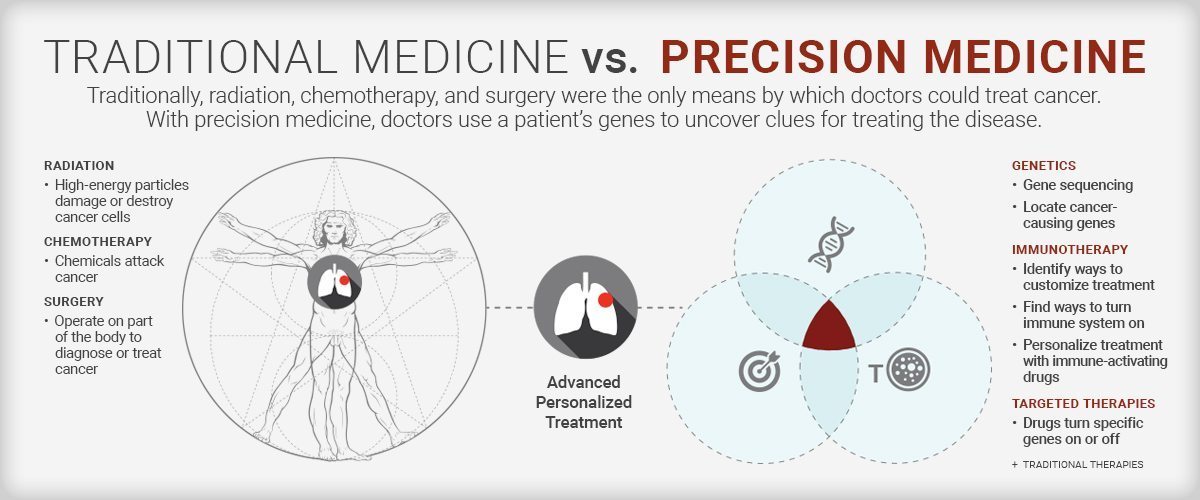
Why Precision Medicine is Essential in Modern Healthcare
Precision medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by shifting the focus from a one-size-fits-all approach to highly individualized treatment strategies. Here’s why it matters:
1. Targeted Treatments for Better Outcomes
Precision medicine allows clinicians to design treatments tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. For example, in oncology, genomic profiling identifies mutations driving cancer, enabling targeted therapies like HER2 inhibitors for breast cancer or KRAS inhibitors for colorectal cancer. These advancements lead to higher success rates and fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
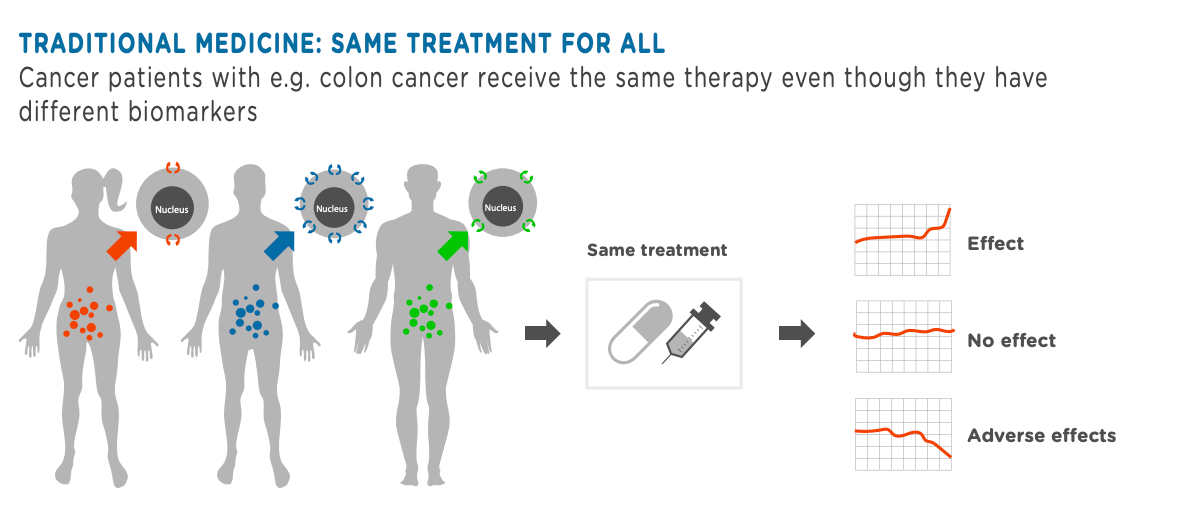
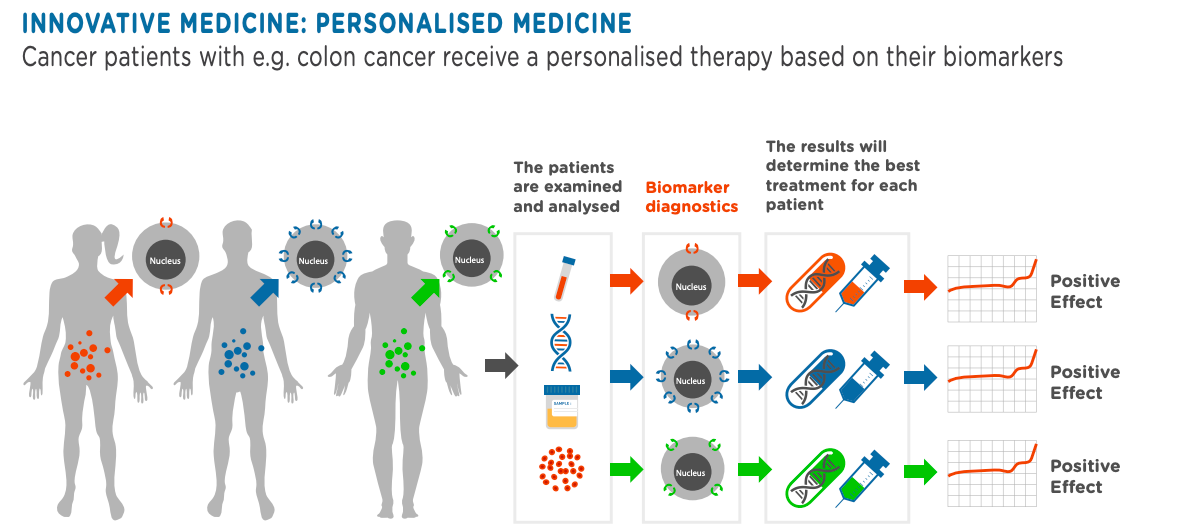
2. Preventive Care and Early Interventions
By leveraging genetic screening and AI-driven predictive analytics, precision medicine helps identify individuals at risk for chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease. This early detection empowers preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes or preemptive therapies, reducing disease burden and healthcare costs.

3. Economic and Systemic Efficiency
Precision medicine reduces the trial-and-error method of prescribing drugs, minimizing unnecessary treatments and hospitalizations. According to a report by Deloitte, precision medicine could save billions by optimizing drug development pipelines and improving patient care efficiency.
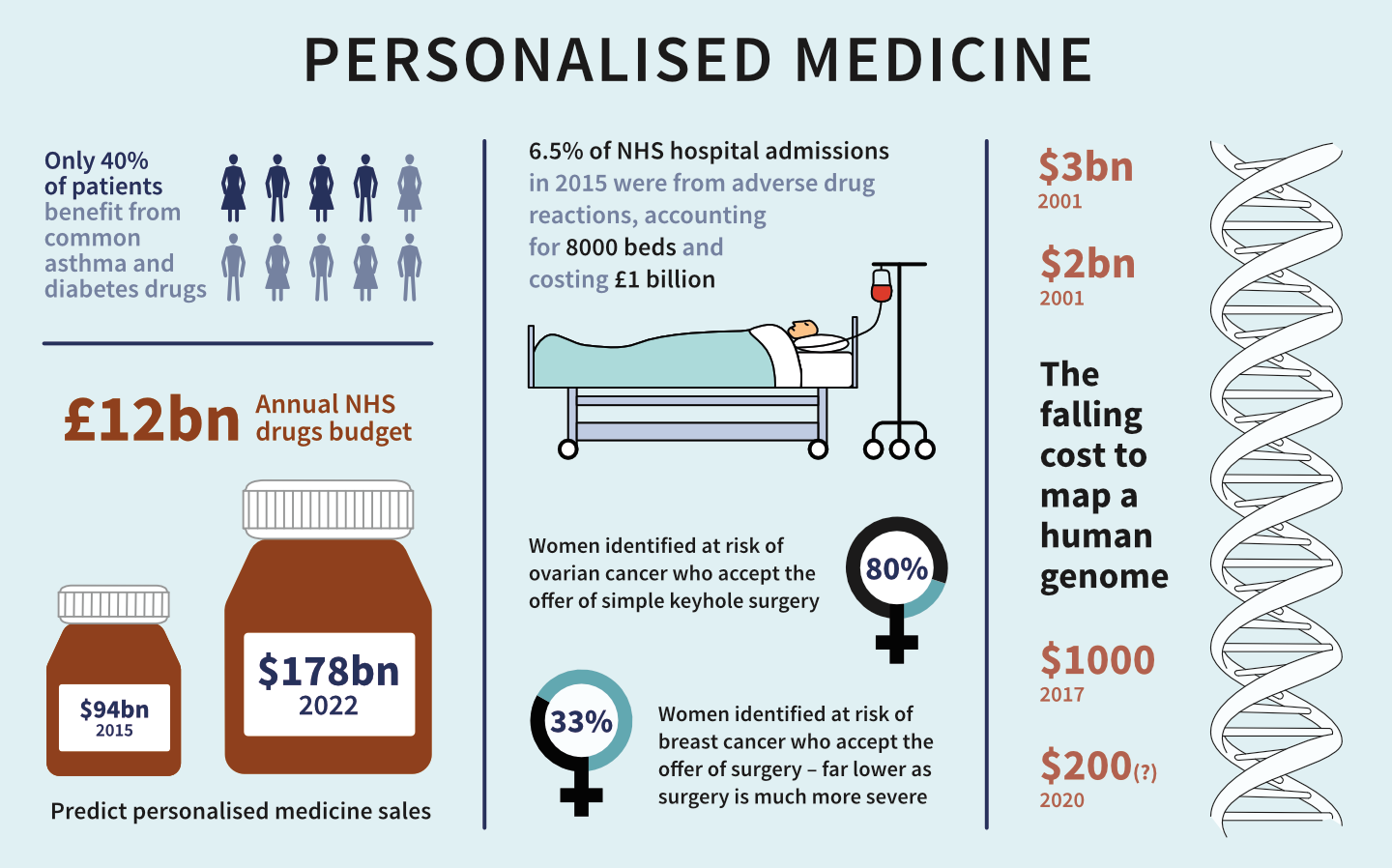
4. Personalized Experiences Enhance Patient Engagement
When patients feel their care is uniquely tailored to them, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, improving health outcomes. This is especially critical in chronic disease management, where adherence to therapies determines long-term success.
5. Global Health Implications
Precision medicine also holds promise in addressing health disparities by creating culturally sensitive treatments. For instance, sickle cell anemia, prevalent in African populations, is now being addressed through gene therapies tailored to its genetic basis, opening avenues for equitable care worldwide.
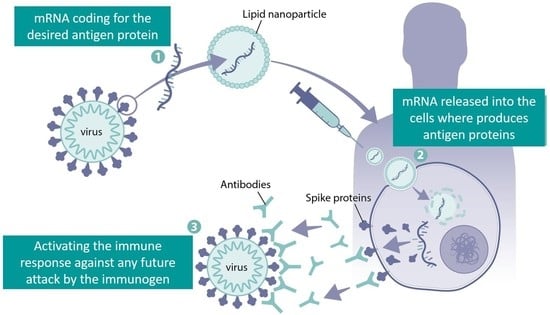
Case in Point: The COVID-19 Response
The rapid development of mRNA vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, showcases the power of precision medicine. These vaccines were designed using genomic information from the virus and quickly adapted for variants, underscoring precision medicine’s ability to address emerging global health crises.
By enabling more effective, efficient, and equitable healthcare, precision medicine isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a moral imperative for the future of health systems worldwide.
How the US is Shaping the Future of Personalized Care
- Government Investment: NIH’s FY25 budget9 earmarks $541 million10 for the All of Us program, a pioneering effort to expand precision medicine initiatives. Precision medicine focuses on tailoring medical treatments to individual patients based on their genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors. This funding will support the diversification of participant data and facilitate new enrollments, with a goal of including pediatric participants by 2026.

- Tech Integration: Robust collaboration between healthcare and Silicon Valley has fostered AI-driven tools for diagnosis and treatment planning.
AI-assisted genomic analysis can lead to a 20% faster diagnosis rate13 for rare diseases, expediting the U.S.’s commitment to accelerating care.
Transformative Technologies Shaping Care
Case Study #1: Tempus – Harnessing Big Data for Personalized Care
Tempus14, a leading technology company in the precision medicine space, specializes in gathering and analyzing clinical and molecular data at scale. Their platform uses AI to provide oncologists with insights into patient-specific treatment plans. By 2023, Tempus had built one of the largest libraries of molecular and clinical data, paired with an advanced operating system to accelerate decision-making in oncology.
- Tempus’ platform reportedly helps reduce trial-and-error prescribing, cutting down treatment mismatches.
- According to a study published in Nature Biotechnology, Tempus’ AI-driven insights resulted in 92% of patients being matched to precision therapies supported by all levels of therapeutic evidence tiers. Of these, 30% of patients matched to targeted therapies supported by high levels of clinical evidence from consensus guidelines or well-powered studies16.
By making actionable insights available at the point of care, Tempus exemplifies how precision medicine can align advanced data analytics with real-world clinical needs.
Case Study #2: Grail – Early Detection of Cancer
Grail17 has revolutionized cancer care through its multi-cancer early detection (MCED) test, Galleri.
Using next-generation sequencing and machine learning, the test identifies early-stage cancers by analyzing DNA fragments shed into the blood (cfDNA).
- In clinical studies, the Galleri-MCED test has shown overall sensitivity of 27·5% for early-stage cancer (stage 1–2). This figure is based on performance in patients with symptomatic disease and is likely to overestimate the screening performance. The test sensitivity was improved to 52·8% by restricting analysis to a set of 12 cancers the Galleri authors specified as being of high unmet need19.
- It identifies over 50 cancer types, 45 of which currently lack standard screening methods. The early detection improves survival rates. Published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention20, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, the analysis used epidemiologic modeling to estimate the potential impact of adding an annual multi-cancer early detection blood test, such as GRAIL’s Galleri™estimates a potential reduction in late-stage (stage III and IV) cancer diagnoses by more than half in the U.S. population, aged 50-79. This decrease in late-stage diagnoses could translate to a reduction in five-year cancer deaths by 39% among those detected earlier, equating to an overall reduction of all five-year cancer deaths by 26%21.
Grail’s groundbreaking work underscores precision medicine’s potential to shift healthcare from reactive to preventive models, saving lives and healthcare costs globally.

Case Study #3: Moderna – Revolutionizing Vaccination with mRNA
Moderna23 became a household name during the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrating the power of precision medicine in vaccine development. Their mRNA-based technology platform enabled the rapid design, testing, and production of vaccines tailored to the genetic sequence of SARS-CoV-2.
- Within a year of the pandemic’s onset, Moderna’s vaccine achieved 94.1% efficacy in clinical trials25.
- Moderna’s mRNA pipeline reflects a myriad of treatment options in various stages of preclinical and commercial development for infectious diseases, latent & public health concerns and therapeutics26.
Moderna’s mRNA platform is now being applied to other diseases, including cancer and rare genetic disorders, showing how precision medicine can reshape global healthcare paradigms.
Challenges in the U.S. Ecosystem
While innovation abounds, systemic challenges remain:
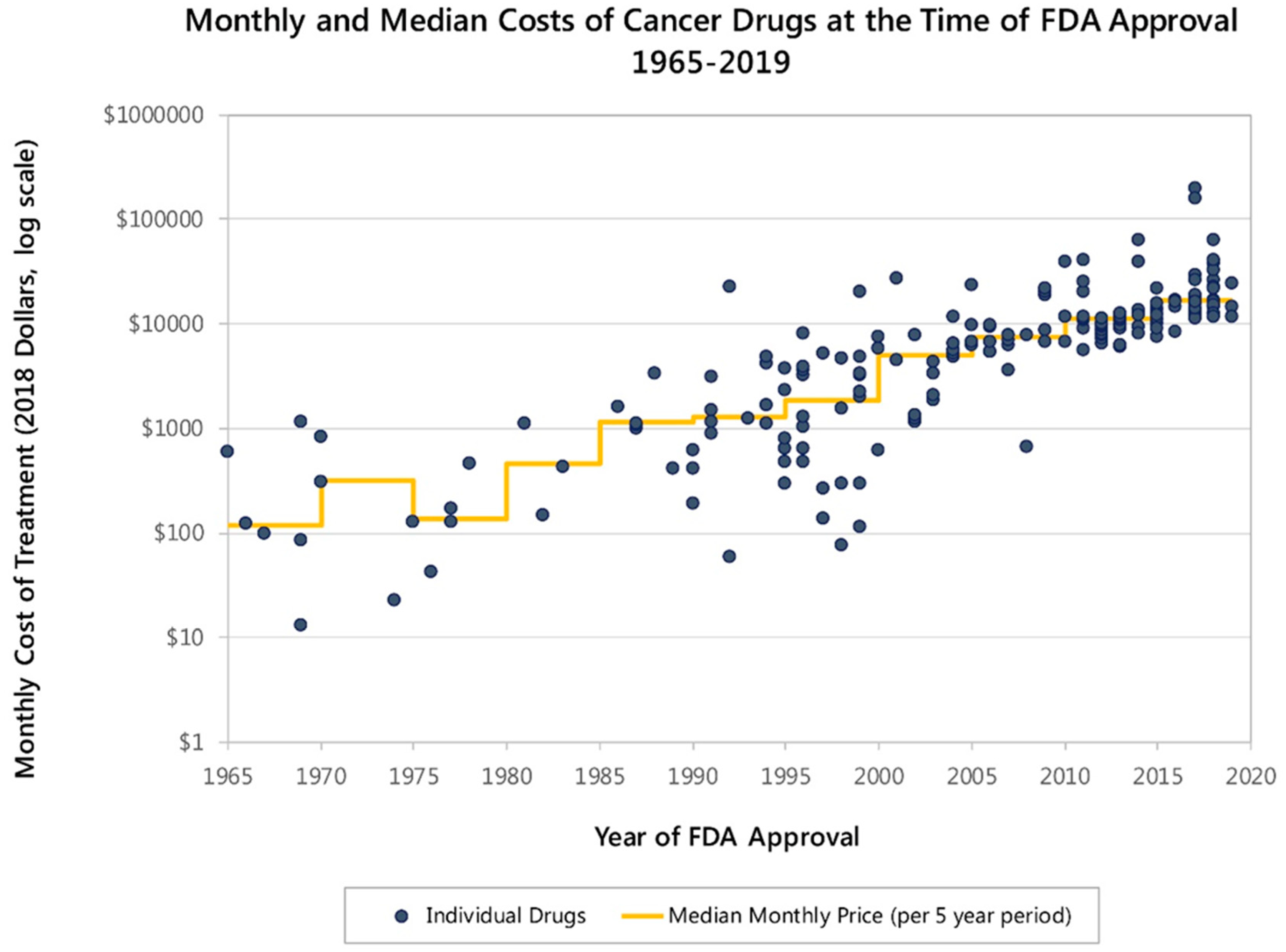
- Cost and Accessibility: Personalized therapies often carry price tags exceeding $100,000, limiting access.
- Data Privacy: Ethical concerns arise over the ownership and use of genetic data.
- Healthcare Equity: Disparities in access persist, particularly in rural and underserved communities.

Efforts are underway to address these issues, with CMS exploring reimbursement models and companies piloting subscription-based payment plans.
What Lies Ahead in 2025 and Beyond

Short-Term Projections (2025–2027):
In the immediate future, the U.S. will see expanded adoption of precision medicine technologies driven by improved accessibility and coverage by major payers. Key trends include:
- Wider Insurance Coverage: Medicare and private insurers are expected to integrate more precision diagnostics into their reimbursable services, especially in oncology and rare disease areas.
- Hospital Partnerships: Collaborations between biotech firms like Tempus and hospital systems will proliferate, ensuring localized availability of AI-driven treatment recommendations.
- mRNA Advancements: Companies such as Moderna will likely expand precision vaccines targeting flu, RSV, and personalized cancer treatments, increasing consumer trust and uptake.
Patients will gain earlier and more accurate diagnostics with potentially reduced out-of-pocket expenses, especially as coverage becomes standardized.
Medium-Term Projections (2028–2032):
Precision medicine will achieve mainstream integration into the U.S. healthcare infrastructure by 2030, supported by continued investment and regulatory incentives.
- Genomic Data Utilization: Large-scale genomic data initiatives, such as the All of Us Research Program, will directly feed into everyday healthcare, enhancing treatment customization for millions of Americans (National Institutes of Health).
- Expansion Beyond Oncology: Applications will grow in cardiovascular diseases, neurological conditions, and autoimmune disorders, areas with significant patient populations in the U.S. (Harvard Health).
- AI-Driven Predictive Healthcare: Consumer-facing technologies like wearable devices will integrate with precision platforms, providing real-time health monitoring and early intervention options.
These advancements will empower individuals to take proactive roles in their healthcare, improving overall quality of life and life expectancy.
Long-Term Projections (2033–2040):
By 2040, precision medicine will fundamentally transform the U.S. healthcare landscape into a proactive, preventive, and consumer-centric model.
- Fully Personalized Healthcare: Every American’s health journey could be guided by real-time AI insights derived from personal genetic and environmental data.
- Cost-Efficient Healthcare System: Precision medicine will reduce long-term healthcare costs by minimizing hospitalizations and ineffective treatments.
- Equity in Access: Programs to reduce health disparities, particularly among underserved communities, will bring precision care to all demographics across the country.
Precision medicine will evolve from being a luxury offering to a universally accessible standard, ensuring equitable health outcomes and a higher quality of life for all.
Conclusion: A Journey Worth Watching
The U.S. is at the forefront of personalized medicine, setting benchmarks for innovation and patient care. As we explore other regions in subsequent posts, we’ll uncover how different healthcare systems are contributing to this global revolution.
Stay tuned for the next installment, where we delve into Europe’s role in advancing precision medicine. Until then, let’s envision a future where healthcare truly caters to the individual.
References
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/impact-potential-personalized-medicine-market-mira-schneider/ ↩︎
- https://bisresearch.com/insights/The-role-of-precision-medicine-in-modern-healthcare-industry ↩︎
- https://healthmatters.nyp.org/precision-medicine/ ↩︎
- https://www.efpia.eu/about-medicines/development-of-medicines/precision-medicine/ ↩︎
- https://www.efpia.eu/about-medicines/development-of-medicines/precision-medicine/ ↩︎
- https://www.embs.org/jtehm/articles/collaborative-paradigm-preventive-personalized-precision-medicine-point-care-technologies/ ↩︎
- https://www.reprocell.com/blog/5-benefits-of-pm ↩︎
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/3/2700 ↩︎
- https://officeofbudget.od.nih.gov/pdfs/FY25/br/Overview%20of%20FY%202025%20Presidents%20Budget.pdf ↩︎
- https://www.govconwire.com/2024/11/nih-fy25-budget/#:~:text=NIH’s%20FY25%20budget%20earmarks%20$541,wide%20range%20of%20medical%20conditions. ↩︎
- https://viablesynergy.com/nih-info-graphic-on-precision-medicine/ ↩︎
- https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/precision-medicine-trends/ ↩︎
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1098360023008432 ↩︎
- https://www.tempus.com/?srsltid=AfmBOorGkBG677b6vmTByeJmjc2qJzwE-EQKPQh0xNjp8zNAcDmis0In ↩︎
- https://www.youtube.com/@Tempus_AI ↩︎
- https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2019/09/30/1922669/0/en/Nature-Biotechnology-Study-Reveals-That-Tempus-xT-Platform-Increases-Cancer-Patients-Personalized-Therapeutic-Opportunities.html ↩︎
- https://grail.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.youtube.com/@GRAILBio ↩︎
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(23)02830-1/fulltext ↩︎
- https://aacrjournals.org/cebp/article/30/3/460/72416/Modeled-Reductions-in-Late-stage-Cancer-with-a ↩︎
- https://grail.com/press-releases/new-research-suggests-multi-cancer-early-detection-blood-test-could-reduce-late-stage-cancer-diagnoses-by-more-than-half/ ↩︎
- https://jech.bmj.com/content/78/6/345 ↩︎
- https://www.modernatx.com/en-US ↩︎
- https://www.youtube.com/@modernatx ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10628441/#:~:text=In%20November%202020%2C%20Pfizer%20determined,the%20second%20dose%20(5). ↩︎
- https://www.modernatx.com/en-US/research/product-pipeline ↩︎
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/17/4272 ↩︎
- https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/health-care/economic-cost-of-health-disparities.html ↩︎
- https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/precision-medicine/ ↩︎




Leave a comment